LDL cholesterol, also known as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, plays a significant role in our overall health. While cholesterol is essential for various bodily functions, an imbalance in LDL cholesterol levels can lead to adverse health effects. In this article, we will delve into the significance of LDL cholesterol, its associated risks, and effective management strategies.
1. Understanding Cholesterol
1.1 What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol, a waxy substance produced by the liver and found in certain foods, is essential for the body to build healthy cells, produce hormones, aid in digestion, and is transported throughout the body by lipoproteins.
1.2 Types of Cholesterol
There are two primary types of cholesterol: LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, while HDL cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol. While HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, LDL cholesterol can accumulate and form plaque in the arteries.
2. LDL Cholesterol: The Bad Cholesterol
2.1 LDL Cholesterol Explained
LDL cholesterol refers to the cholesterol carried by low-density lipoproteins. These lipoproteins are responsible for transporting cholesterol from the liver to the cells throughout the body. However, if there is an excess of LDL cholesterol or insufficient HDL cholesterol, it can lead to health issues.
2.2 The Role of LDL Cholesterol in Health
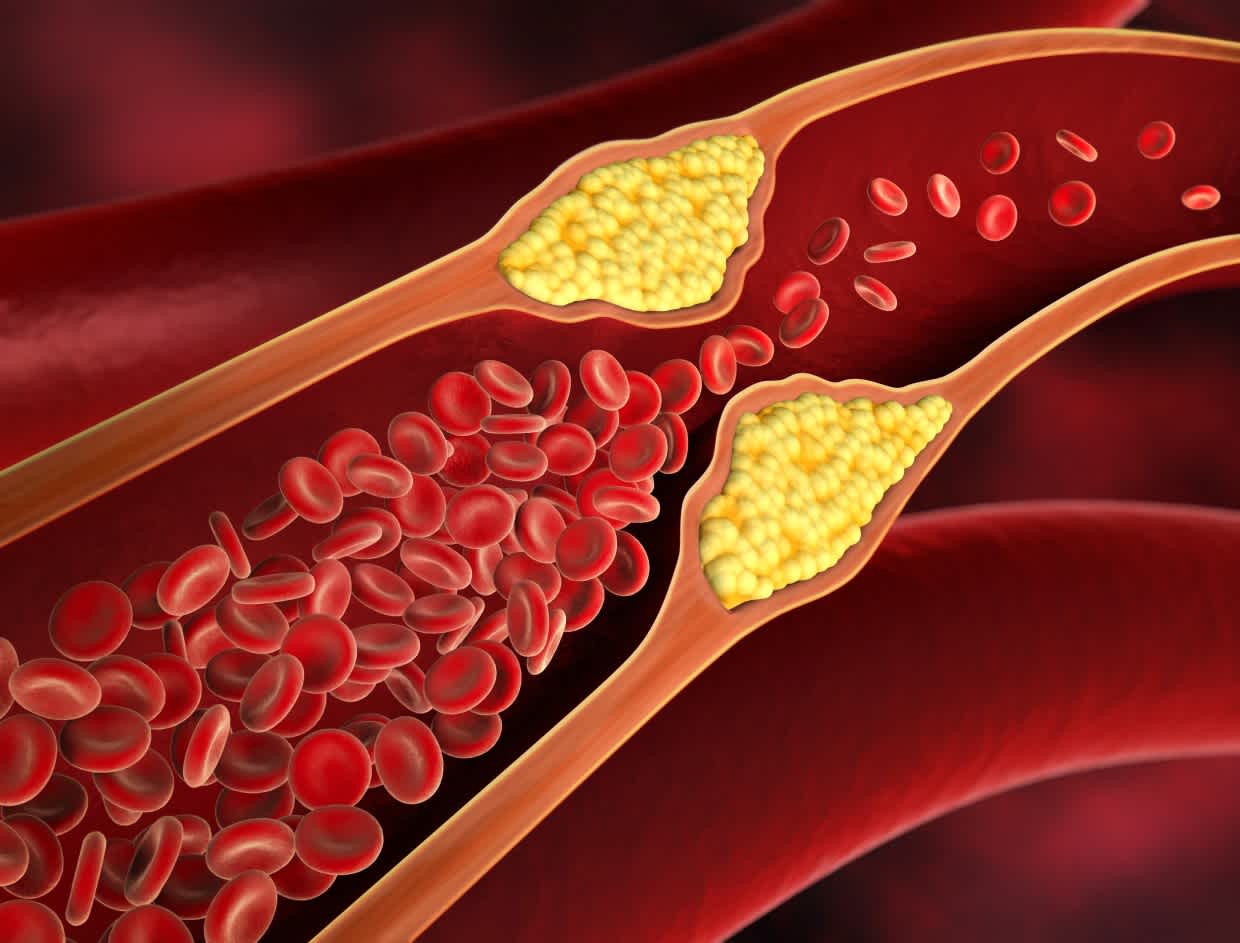
While LDL cholesterol is essential for various bodily functions, high levels of LDL cholesterol can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis occurs when LDL cholesterol builds up in the arteries, forming plaque and narrowing the blood vessels. This condition increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
3. Risks Associated with High LDL Cholesterol
3.1 Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease
The accumulation of LDL cholesterol in the arteries can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of the arteries. Atherosclerosis restricts blood flow, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, angina, and peripheral artery disease.
3.2 Stroke and Heart Attack
When the plaque buildup in the arteries ruptures, it can result in the formation of blood clots. If a blood clot blocks a narrowed artery supplying blood to the heart or brain, it can lead to a heart attack or stroke, respectively.
4. Managing LDL Cholesterol Levels
4.1 Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage LDL cholesterol levels effectively. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, can raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress levels are crucial in managing cholesterol levels.
4.2 Dietary Approaches
A heart-healthy diet can significantly impact LDL cholesterol levels. Incorporating foods rich in soluble fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help lower LDL cholesterol. Limiting the intake of saturated and trans fats, found in fatty meats and processed foods, is also essential.
4.3 Medications for LDL Cholesterol
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage LDL cholesterol levels. Medications such as statins, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, and PCSK9 inhibitors may be prescribed by healthcare professionals to control cholesterol levels effectively.
5. Conclusion
Maintaining healthy LDL cholesterol levels is vital for overall cardiovascular health. By understanding the risks associated with high LDL cholesterol and implementing lifestyle modifications and appropriate medical interventions, individuals can effectively manage their cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart-related complications.
FAQs
Q1: Can LDL cholesterol be too low?
A1: While having low LDL cholesterol levels is generally considered beneficial, extremely low levels may not be ideal as cholesterol is essential for various bodily functions.
Q2: Are there any natural ways to lower LDL cholesterol?
A2: Yes, certain dietary changes like increasing fiber intake, consuming healthy fats, and incorporating plant sterols can help lower LDL cholesterol levels naturally.
Q3: Can exercise help in reducing LDL cholesterol?
A3: Yes, regular exercise can raise HDL cholesterol (the good cholesterol) and lower LDL cholesterol, thereby improving the overall cholesterol profile.
Q4: Are there any side effects of cholesterol-lowering medications?
A4: Some cholesterol-lowering medications may have side effects, but they are generally well-tolerated. It is important to discuss any issues with a healthcare professional.
Q5: How often should cholesterol levels be checked?
A5: It is recommended to have cholesterol levels checked regularly, especially for individuals with a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular diseases.